In a recent article, I covered all of the reasons you might be tempted to hold a highly concentrated position in your company stock as a tech founder and how it fits into your portfolio. I then followed up with a rundown on why resisting diversification is generally a bad idea and the subconscious biases that hold us back from selling.
So now that you understand the benefits of diversification and have taken inventory of your portfolio, what is the most effective way for you to move forward? I will share with you what to keep in mind before selling, how to decide when to sell, and strategies to execute sales such as options, exchange funds, prepaid variable forward contracts, qualified small business stock and tax considerations. Now, let’s take a deep dive into strategic approaches to take as a shareholder and important tax implications to consider.
Keep in mind: Lockups and blackout periods
Most tech companies that IPO have a 180-day lockup period that prevents insiders, employees and VC funds from selling immediately. There is usually language that also prohibits hedging with derivatives (options) during that period. Lockups are intended to help prevent insider trading and provide the company with additional post-IPO price stability.
It is also important to abide by the company’s blackout periods, which prohibit transactions during more share-price-sensitive times, such as earnings or material nonpublic information releases.
Concentrated stock strategies
Ad hoc selling — This is the most straightforward and involves the outright sale of your shares. However, this can be difficult for various reasons such as selling restrictions, the perception by others that you are unloading stock and many psychological biases that act as internal mental obstacles.
Scheduled selling — Selling all your stock at once could be both emotionally challenging and tax-inefficient. Scheduled selling involves the selling of a set number of shares over a specific period. This selling strategy can help by spreading the tax impact over a few years. It also provides an advantage from a psychological standpoint since the plan is determined upfront, then mechanically executed.
As an example, a founder might plan to sell 500,000 shares over 18 months. The founder is comfortable selling quarterly, which equals six selling periods of 83,333 shares per quarter. In a scenario where a founder is subject to blackout periods, a 10b5-1 trading plan can be implemented and set on autopilot. The company may even allow you to sell your shares during blackout periods with a 10b5-1 trading plan. See the example of scheduled selling below.
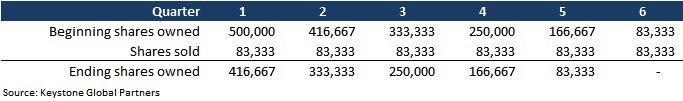
Image Credits: Keystone Global Partners
Hedging with options — Multiple hedging strategies can be implemented to protect your downside; however, some of the more common approaches used are the protective put and the protective collar. Below are basic examples of how these strategies are executed, for illustrative purposes.
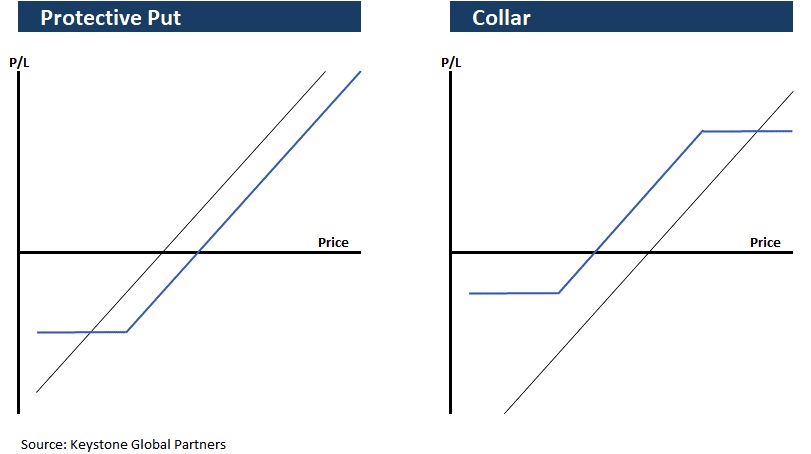
Image Credits: Keystone Global Partners
- Protective put: Buying protection against the downside.
- Collar: Give up some upside to limit some downside.
Each strategy allows the owner to continue holding the stock while providing some downside protection against a stock’s decline. However, these strategies are not tax-efficient and are complicated, so working with an expert is essential. Both puts and certain types of collars would have been extremely expensive to implement during the recent market crisis because market volatility is a factor in options prices. See the below chart of the VIX (volatility index) during peak crisis. However, in some instances, these strategies can make sense.

